
SL Paper 1
Which statements are correct?
I. The activation energy of a reaction is not affected by temperature.
II. A catalyst reduces the enthalpy change of a reaction.
III. Catalysts provide alternative reaction pathways.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
A student was investigating rates of reaction. In which of the following cases would a colorimeter show a change in absorbance?
A. KBr (aq) + Cl2 (aq)
B. Cu (s) + Na2SO4 (aq)
C. HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq)
D. (CH3)3COH (aq) + K2Cr2O7 (aq)
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
Question 17 was the question about the colorimeter), which many teachers felt was unfair, and only 22% of students gave the correct answer. The complaints about the question were often based on the lack of familiarity with the colorimeter. However, Chemistry is a practical course and student should be exposed to a piece of equipment such as this. Also, it was felt that there was a lot to process in this question. Although answer C could fairly easily be eliminated as there is no colour change. Students then had to recognize that in D, alcohol oxidation would result in a colour change from orange to green, except that it is a tertiary alcohol. This left A and B. A is of course the right answer as chlorine replaces bromine, but if B actually happened, there would also be a colour change from clear to blue. So, students needed to remember that copper is below sodium on the activity series.
The dotted line represents the formation of oxygen, O2(g), from the uncatalysed complete decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 (aq).
Which curve represents a catalysed reaction under the same conditions?
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
Graphical representation of catalysis was also well answered.
Several reactions of calcium carbonate with dilute hydrochloric acid are carried out at the same temperature.
CaCO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) → CaCl2 (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g)
Which reaction has the greatest rate?
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
65 % of the candidates chose the correct combination to give the greatest rate of reaction. The most commonly chosen distractor was D where “smaller surface area of same mass of CaCO3(s)” was chosen. It seems these candidates confused “surface area” with “particle size”.
Which properties can be monitored to determine the rate of the reaction?
Fe (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → Cu (s) + FeSO4 (aq)
I. change in volume
II. change in temperature
III. change in colour
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
One G2 form queried if visible spectroscopy is on the core syllabus and therefore should candidates be aware of monitoring a reaction via colour change. However, 6.1 clearly states that following change in colour is one method of following reactions.
Which experimental methods could be used to observe the progress of the following reaction?
Cr2O72-(aq) + 6I-(aq) + 14H+(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 3I2(aq) + 7H2O(l)
I. Change in colour
II. Change in mass
III. Change in electrical conductivity
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
For the reaction R → P, which letter represents the activation energy for the catalysed reverse reaction?
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
Which methods can be used to monitor the progress of this reaction?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
Which change does not increase the initial rate of reaction when CaCO3(s) is added to excess HCl(aq)?
A. Decrease in the size of the CaCO3(s) particles
B. Increase in the temperature of the reaction mixture
C. Increase in the concentration of HCl(aq), keeping the same volume
D. Increase in the volume of HCl(aq), keeping the same concentration
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
On the following Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution, which letter represents activation energy?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
100 cm3 of 10% hydrogen peroxide solution decomposes at 298 K to form water and oxygen.
H2O2(aq) → H2O(l) + O2(g)
The dotted line graph represents the volume of oxygen produced.
Which graph represents the decomposition of an equal volume of a 20% solution under the same conditions?
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
Which arrow shows the activation energy of the uncatalysed forward reaction for this equilibrium?
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
Identifying the activation energy of an uncatalyzed reaction from an energy profile diagram was the best answered question in the exam.
The graph shows the Maxwell–Boltzmann energy distribution curve for a given gas at a certain temperature.
How would the curve change if the temperature of the gas decreases while the other conditions remain constant?
A. The maximum would be lower and to the left of M.
B. The maximum would be lower and to the right of M.
C. The maximum would be higher and to the left of M.
D. The maximum would be higher and to the right of M.
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
The diagram shows the energy profile for a catalysed and uncatalysed reaction.
Which represents the enthalpy change, ΔH, and the activation energy, Ea, for the catalysed reaction?
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
Which factors can affect the rate of reaction?
I. Particle size of solid reactant
II. Concentration of reacting solution
III. Pressure of reacting gas
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Samples of sodium carbonate powder were reacted with separate samples of excess hydrochloric acid.
Na2CO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) → CO2 (g) + 2NaCl (aq) + H2O (l)
Reaction I: 1.0 g Na2CO3 (s) added to 0.50 mol dm−3 HCl (aq)
Reaction II: 1.0 g Na2CO3 (s) added to 2.0 mol dm−3 HCl (aq)
What is the same for reactions I and II?
A. Initial rate of reaction
B. Total mass of CO2 produced
C. Total reaction time
D. Average rate of production of CO2
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
Which apparatus can be used to monitor the rate of this reaction?
- A pH meter
- A gas syringe
- A colorimeter
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
It was pleasing to see that a vast majority of candidates could select equipment necessary to monitor rates of reaction. This was one of the best answered questions in the exam.
Copper catalyses the reaction between zinc and dilute sulfuric acid.
Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Why does copper affect the reaction?
A. Decreases the activation energy
B. Increases the activation energy
C. Increases the enthalpy change
D. Decreases the enthalpy change
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
Curve 1 shows the mass change when marble chips are added to excess hydrochloric acid in an open beaker.
Which changes would produce curve 2?
A. Powdering the marble chips and heating
B. Powdering the marble chips and doubling their mass
C. Doubling the volume of acid and heating
D. Doubling the acid concentration and powdering the marble chips
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
Which change increases the rate of formation of hydrogen when zinc reacts with excess hydrochloric acid, assuming all other conditions remain the same?
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
A. Adding water to the hydrochloric acid
B. Decreasing the temperature
C. Increasing the volume of hydrochloric acid
D. Decreasing the size of the zinc particles while keeping the total mass of zinc the same
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
What decreases the activation energy of a reaction?
A. Increasing the temperature
B. Adding a catalyst
C. Adding more reactants
D. Increasing collision frequency of reactants
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
Excess magnesium powder was added to a beaker containing hydrochloric acid, HCl (aq).
The mass of the beaker and its contents was recorded and plotted against time (line I).
Which change could give line II?
A. Doubling the mass of powdered Mg
B. Using the same mass of Mg ribbon
C. Increasing the temperature
D. Using the same volume of more concentrated HCl
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Which change causes the greatest increase in the initial rate of reaction between nitric acid and magnesium?
2HNO3 (aq) + Mg (s) → Mg(NO3)2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
The potential energy profile for the reversible reaction, X + Y Z is shown.
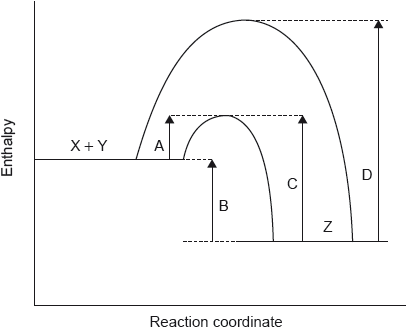
Which arrow represents the activation energy for the reverse reaction, Z → X + Y, with a catalyst?
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
A reaction has an activation energy of 40 kJ mol−1 and an enthalpy change of −60 kJ mol−1.
Which potential energy diagram illustrates this reaction?
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
Very well answered. 82% of the candidates selected the potential energy diagram with the correct activation energy and enthalpy change to represent the reaction.
Which instrument would best monitor the rate of this reaction?
2KI (aq) + Cl2 (aq) → 2KCl (aq) + I2 (aq)
A. Balance
B. Colorimeter
C. Volumetric flask
D. Gas syringe
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
Which is the activation energy of the forward reaction?
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
Well answered. 88 % of the candidates chose the correct arrow representing the activation energy of the forward reaction.
The graph shows the Maxwell–Boltzmann energy distribution curve for a given gas at a certain temperature.
How will the curve change if the temperature of the gas is increased, while other conditions remain constant?
A. The maximum is higher and to the left of A.
B. The maximum is higher and to the right of A.
C. The maximum is lower and to the right of A.
D. The maximum is lower and to the left of A.
Markscheme
C
Examiners report
The dotted line represents the volume of carbon dioxide evolved when excess calcium carbonate is added to hydrochloric acid.
Which graph represents the production of carbon dioxide when excess calcium carbonate is added to the same volume of hydrochloric acid of double concentration?
Markscheme
D
Examiners report
Which combination has the greatest rate of reaction at room temperature?
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
A sample of calcium carbonate reacts with excess hydrochloric acid in a beaker. The solid line shows how the mass of the beaker changes with time.
Which dashed line represents the results obtained when the acid concentration is doubled?
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
The same amount of two gases, X and Y, are in two identical containers at the same temperature. What is the difference between the gases?
A. X has the higher molar mass.
B. Y has the higher molar mass.
C. X has the higher average kinetic energy.
D. Y has the higher average kinetic energy.
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
This was by far the most challenging question on the paper, answered correctly by only 19 % of the candidates. Some teachers thought this was beyond the scope of the syllabus while others thought it was a question requiring thought. To be able to answer, candidates needed to connect kinetic energy to the speed and mass of the molecule.
Why does a reaction for a sample of gases, at constant temperature, occur faster at higher pressure?
A. Collisions are more frequent.
B. Collisions are more energetic.
C. High pressure lowers activation energy.
D. The reaction is more exothermic at high pressure.
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
A very well-answered question in which 90% of the candidates related the effect of higher pressure on the rate of reaction of gaseous reactants to the collision theory correctly.
Which will increase the rate of reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid?
I. an increase in temperature
II. an increase in concentration of hydrochloric acid
III. an increase in particle size of calcium carbonate
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Markscheme
A
Examiners report
One teacher pointed out that the question should have stated for a fixed mass of calcium carbonate. However, this question was one of the highest scoring so it did not cause confusion.